Camshaft Timing Drive Components Cleaning and Inspection
Cleaning Procedure
Clean all the following components with solvent:
- Camshaft sprockets
- Intermediate sprocket
- Crankshaft sprocket
- Primary timing chain
- Secondary timing chains
- Primary timing chain guide
- Secondary timing chain guides
- Primary timing chain shoe
- Secondary timing chain shoes
- Primary timing chain tensioner
- Secondary timing chain tensioners
- Timing component fastening bolts
Caution: Wear safety glasses in order to avoid eye damage.
Dry the timing components with compressed air.
Visual Inspection
Camshaft Sprockets
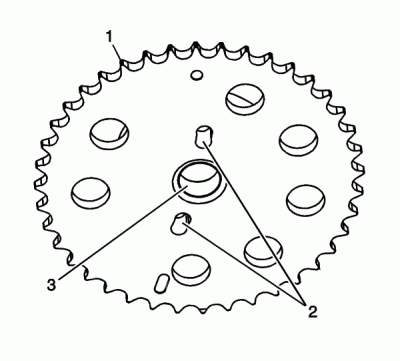
Inspect the front of the left exhaust and intake camshaft sprockets for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Camshaft locating pin hole damage (2)
- Mounting bolt hole damage (3)
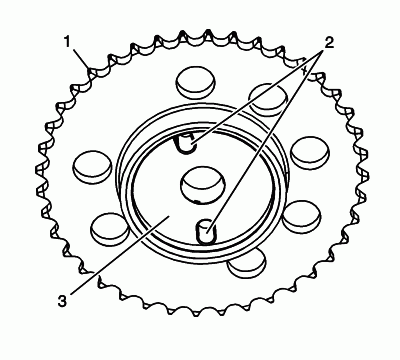
Inspect the back of the left exhaust and intake camshaft sprockets for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Camshaft locating pin hole (2)
- Camshaft seating/sealing inner hub flange damage (3)
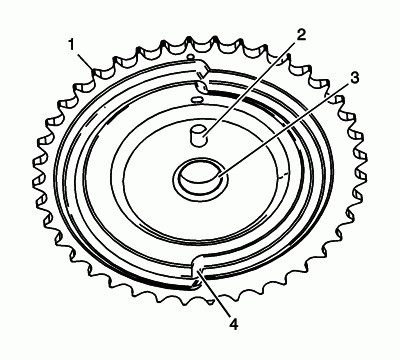
Inspect the front of the right exhaust camshaft sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Camshaft locating pin hole damage (2)
- Mounting bolt hole damage (3)
- Camshaft position sensing ring damage (4)
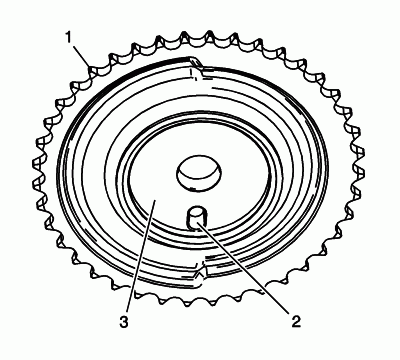
Inspect the back of the right exhaust camshaft sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Camshaft locating pin hole (2)
- Camshaft seating/sealing inner hub flange damage (3)
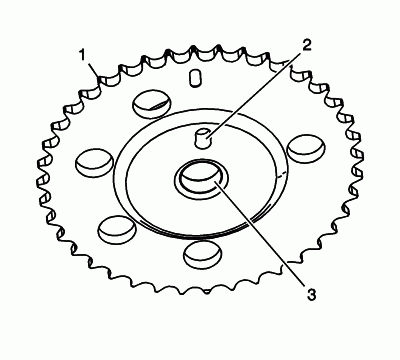
Inspect the front of the right intake camshaft sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Camshaft locating pin hole damage (2)
- Mounting bolt hole damage (3)
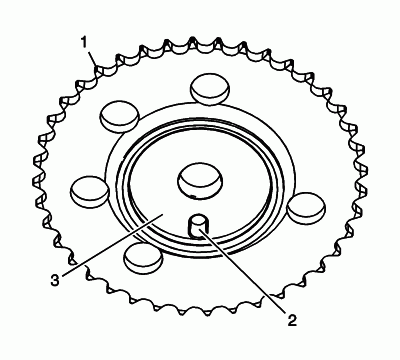
Inspect the back of the right intake camshaft sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Camshaft locating pin hole (2)
- Camshaft seating/sealing inner hub flange damage (3)
Replace a damaged camshaft position actuator.
Intermediate Sprocket
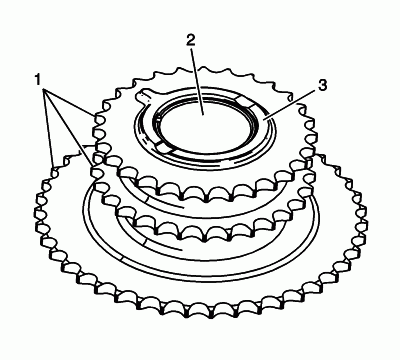
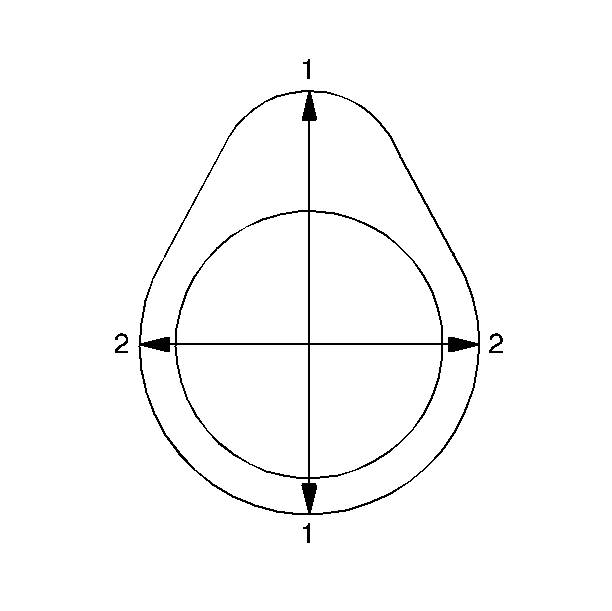
Inspect the front of the intermediate sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Bearing bore damage (2)
- Thrust surface damage (3)
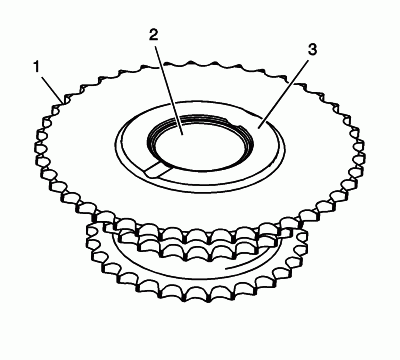
Inspect the back of the intermediate sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Bearing bore damage (2)
- Thrust surface damage (3)
Replace a damaged intermediate sprocket.
Crankshaft Sprocket
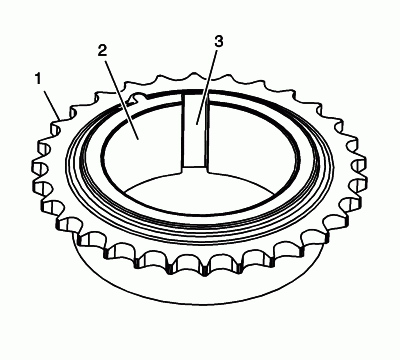
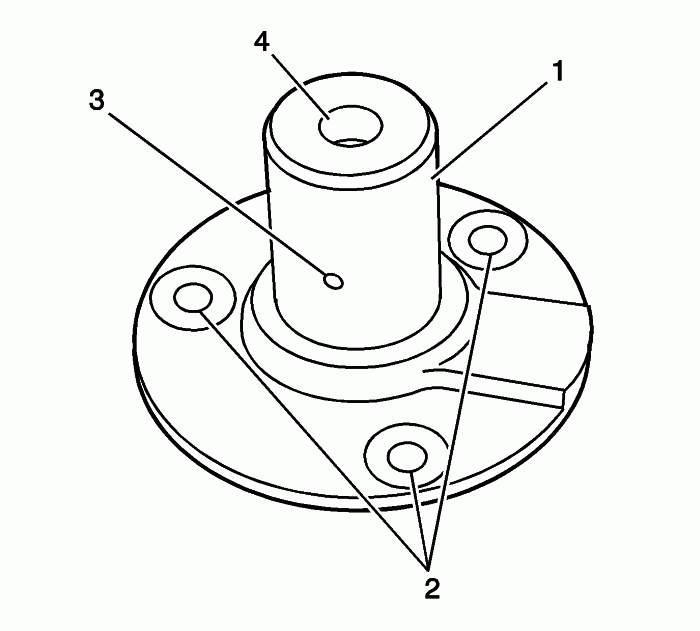
Inspect the intermediate sprocket for the following:
- Sprocket damage (1)
- Bore damage (2)
- Keyway damage (3)
Replace a damaged crankshaft sprocket.
Primary and Secondary Timing Chains
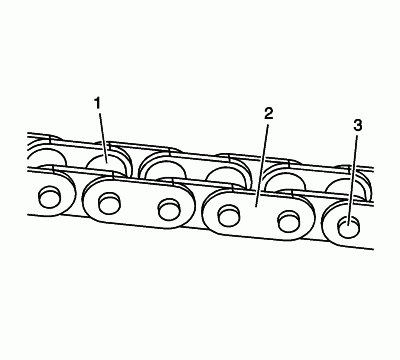
Inspect the primary and/or secondary timing chain for the following:
- Binding or worn rollers (1)
- Loose links (2)
- Loose pins (3)
Replace a damaged primary and/or secondary timing chains.
Primary Timing Chain Guide
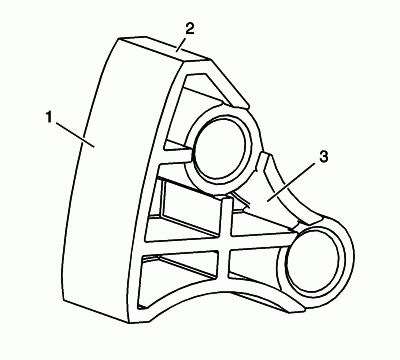
Inspect the primary timing chain guide for the following:
- Worn guide surface (1)
- Cracked or broken guide surface (2)
- Cracked or damaged guide base (3)
Replace a damaged primary timing chain guide.
Secondary Timing Chain Guides
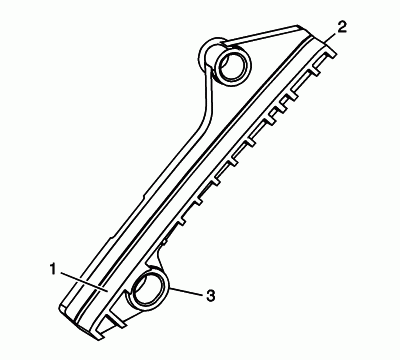
Inspect the secondary timing chain guides for the following:
- Worn guide surface (1)
- Cracked or broken guide surface (2)
- Cracked or damaged guide base (3)
Replace a damaged secondary timing chain guide.
Secondary Timing Chain Shoes
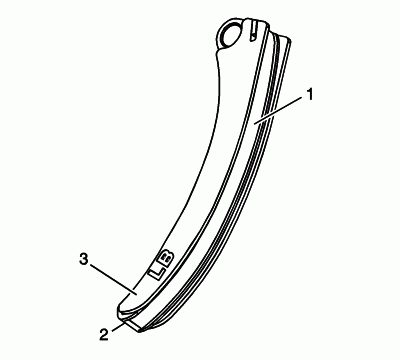
Inspect the secondary timing chain shoes for the following:
- Worn shoe surface (1)
- Cracked or broken shoe surface (2)
- Cracked or damaged shoe (3)
Replace a damaged secondary timing chain shoe.
Primary Timing Chain Tensioner
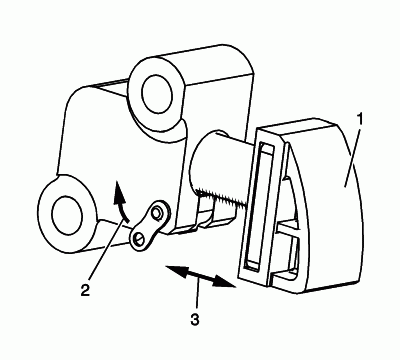
Inspect the primary timing chain tensioner for worn primary timing chain tensioner shoe surface (1).
Inspect the primary timing chain tensioner for locked or binding timing chain tensioner. Release the locking lever (2) and ensure the plunger moves freely (3) in and out of the body of the tensioner.
Replace a damaged primary timing chain tensioner.
Secondary Timing Chain Tensioners
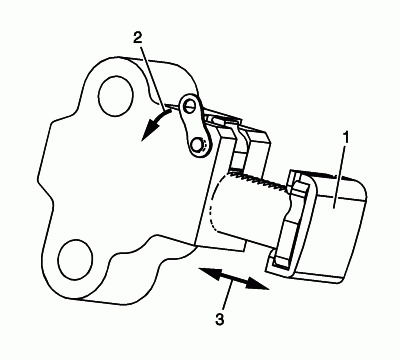
Inspect the secondary timing chain tensioner for damaged plunger-to-shoe contact surface (1).
Inspect the secondary timing chain tensioner for locked or binding timing chain tensioner. Release the locking lever (2) and ensure the plunger moves freely (3) in and out of the body of the tensioner.
Replace a damaged primary and/or secondary timing chain tensioner.
Timing Component Fasteners
Inspect the timing component fasteners.
Replace any damaged timing component fasteners, do not repair.